| 印刷電路板 | ||
|
|
醫療應用 | |
| 磁芯上的應用 | ||
| 橡膠上的應用 | ||
| 微電子/微馬達 | ||
聚對二甲苯不僅電性能、防護性能好,而且生物相容性也好,它已通過美國FDA 論證,滿足美國藥典生物醫用材料VI 類標準,被列為是一種可以在體內長期植入使用的生物醫用材料。隨著生物醫用電子科學的不斷進步和發展,在國外除了心臟起搏器用聚對二甲苯進行可靠絕緣防護外,腦電極、植入式感測器、射頻治療儀、血液分析感測器和高頻手術刀等微型電子醫療器械,也都有使用聚對二甲苯的報道。
Parylene - Gas Phase Medical Coating for Unparalleled Performance
-
"The silicone tubing we’re using is perfect for the
application...but it is quite tacky. Without the Parylene coating, it
felt terrible, and the surgeons hated it."
- "Now that we’ve solved the trocar-to-cannula friction issues with a Parylene coating, these disposable trocar/cannula sets are splendid, inexpensive devices. No insertion/withdrawal stutter motion at all."
Parylene, a Biostability, Biocompatibility, Medical
Coating
SCS Parylene medical coating provides an inert biocompatible
barrier to chemicals, moisture and biofluids; Parylene adds dry film
lubricity; and is recognized as a Class VI polymer by the FDA.
 Because their polymeric backbone is made
entirely of carbon, Parylene is not vulnerable to hydrolytic breakdown in
the corrosive aqueous implantation environment. Hence, they are highly
regarded as candidates for implantation survival. In the VDP process, a
highly reactive monomer spontaneously polymerizes at room temperature
without need for a catalyst. Conventional coating systems that are dipped,
sprayed, or brushed require catalysts and elevated temperature cure cycles
to improve coating properties to acceptable levels. Since Parylene
coatings require no elevated temperature cure cycle, there are no
associated cure stresses. Other coating systems may start with proprietary
formulations that include solvents, fillers, stabilizers, plasticizers,
and the like. Along with the chemical residues of the polymerization
catalyst, these ingredients represent potentially mobile components in the
final coating that may be outgassed or extracted. Thin, uniform, and
transparent, Parylene coatings deposit in a predictable and understandable
manner inside tubes or deep crevices. At the entrance, coatings are the
same thickness as on the outside. Surfaces further from the entrance
receive thinner coatings. The thickness of Parylene coatings is
controllable from below 100 nanometers to several mils. Parylene coatings
can provide strength and support to very thin, fragile substrates. They
contribute these properties with minimal mass because the required coating
thick-ness can be applied reliably to all surfaces.
Because their polymeric backbone is made
entirely of carbon, Parylene is not vulnerable to hydrolytic breakdown in
the corrosive aqueous implantation environment. Hence, they are highly
regarded as candidates for implantation survival. In the VDP process, a
highly reactive monomer spontaneously polymerizes at room temperature
without need for a catalyst. Conventional coating systems that are dipped,
sprayed, or brushed require catalysts and elevated temperature cure cycles
to improve coating properties to acceptable levels. Since Parylene
coatings require no elevated temperature cure cycle, there are no
associated cure stresses. Other coating systems may start with proprietary
formulations that include solvents, fillers, stabilizers, plasticizers,
and the like. Along with the chemical residues of the polymerization
catalyst, these ingredients represent potentially mobile components in the
final coating that may be outgassed or extracted. Thin, uniform, and
transparent, Parylene coatings deposit in a predictable and understandable
manner inside tubes or deep crevices. At the entrance, coatings are the
same thickness as on the outside. Surfaces further from the entrance
receive thinner coatings. The thickness of Parylene coatings is
controllable from below 100 nanometers to several mils. Parylene coatings
can provide strength and support to very thin, fragile substrates. They
contribute these properties with minimal mass because the required coating
thick-ness can be applied reliably to all surfaces.
Biostability and Biocompatibility
Parylene N and Parylene C are certified to comply with the USP biological testing requirements for Class VI Plastics, which include Acute Systemic Toxicity, Irritation/Intracutaneous Reactivity, and Implantation. Culture studies using diploid WI-38 embryonic human lung cells have demonstrated that Parylene C coatings are highly compatible with living cells, with little evidence of cytotoxicity. In vitro tissue culture studies show that human cell types readily proliferate on Parylene C coated surfaces to produce thin, adherent layers of morphologically normal tissue. Successful in vivo cell growth studies have also been reported. Parylene C has been used to coat and anchor experimental fabrics used as scaffolding for the growth of blood compatible intimal linings for experimental circulatory assist devices. The acute toxicity of the Parylene dimers, the precursor materials used to prepare Parylene coatings have also been found to be low. Specialty Coating Systems maintains Parylene Drug and Device Master Files with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. These files, containing the results of biological studies on Parylene, are available for reference by all SCS coating service customers.
Barrier Properties
Functionally, Parylene is a pinhole-free barrier against moisture, chemical, and biofluid and biogases. As with all coatings, Parylene has small but measurable permeabilities to molecules such as water and the common gases. While the Parylenes’ water vapor transmission rate has been found to be significantly lower than most conventional coatings. (Below: The effect of Parylene C coating thickness on extractable metals from rubber specimens)
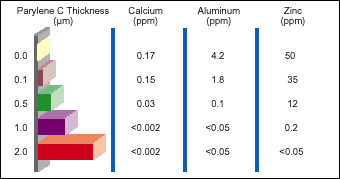
In a series of experiments, rubber test specimens were autoclaved for one hour in one molar hydrochloric acid, and the acid extracts were then analyzed by atomic absorption spectrometry for certain metals known to be present in the rubber’s additive systems: calcium, aluminum, and zinc. Parylene coatings on the test specimens markedly decreased extraction of these metals.
Lubricity
Parylene possesses excellent dry film lubricant characteristics. Lubricity, as indicated by coefficient of friction (COF) measurements, approaches that of TEFLON®. In a special measurement of lubricity, a stainless steel plate was positioned so that its angle of inclination with respect to horizontal could be adjusted and locked. Rubber specimens were fixtured in a 256 gram weight such that they lay on the stainless steel plate. The incline of the plate was then increased until the weight commenced to slide, at which point the plate was locked and the angle recorded. The tangent of the angle of inclination, is the static COF for the Parylene coated rubber specimen. The test was repeated with rubber specimens having different thicknesses of Parylene C coatings, and the results were compared with uncoated and silicone coated specimens. This figure illustrates that Parylene C significantly improves the lubricity of the rubber specimens. The COF for Parylene C, as measured by ASTM D 1894, is 0.29 for both static and dynamic observations.
Dielectric Properties
Parylene is an excellent electrical insulator. Its dielectric constant is relatively independent of frequency and temperature, while the dielectric losses are low. SCS Parylenes’ high dielectric strength is attributable to the fact that they can be formed as thin, continuous films free from defects and the fillers commonly found in conventional coatings, both of which tend to reduce dielectric strength.
|
Table 1 - Parylene N and C differ
somewhat in properties, and the optimum
choice is dependent on specific
application requirements.
Parylene Medical Applications
![]()
Parylene coatings have found use in such diverse
applications as temporary surgical hardware, prostheses components,
catheters, stoppers, probes, needles, and cochlear implants. These
coatings are also used on mandrels to manufacture catheters, on endoscopic
surgical devices, and on implanted pacemakers and defibrillators.
 Pressure
sensors and ultrasound transducers -
sensitive electronic
devices can be effectively isolated and insulated by a very thin Parylene
coating. This low mass protective coating does not significantly alter the
operation of such devices, yet provides electrical and corrosion
protection.
Pressure
sensors and ultrasound transducers -
sensitive electronic
devices can be effectively isolated and insulated by a very thin Parylene
coating. This low mass protective coating does not significantly alter the
operation of such devices, yet provides electrical and corrosion
protection.
Cardiac assist devices - the delicate electronic components in cardiac pacemakers and implantable defibrillators are sealed against the corrosive effects of biofluids with a Parylene conformal coating. Parylene is also used to electrically isolate the protective metal cases of these implanted devices.
Stents, prostheses, and bone growth stimulator components - metal hardware such as restorative artificial devices can be sealed with Parylene to eliminate problems related to microporosity and to protect against corrosive biofluids. Human cell types readily proliferate on and Parylene coated surfaces to produce thin, morphologically normal tissue.
Catheters, mandrels and molds - molded surgical components such as catheters can be Parylene coated to improve lubricity and protect against the corrosive effects of biofluids. Precise wire forms used in the production of catheters are coated with Parylene. Parylene’s low coefficient of friction aids in mold release, and its conformability assures the quality of the finished catheters.
Needles and Epidural probes - the surface of a brain stimulating electrode is made lubricious, and is selectively insulated. Parylene coats both the inner and outer surfaces of injection needles to seal microporosity and to create a smooth pinhole-free surface that reduces the potential for adherence of contaminants. The throwing power of Parylene N makes it particularly effective in penetrating and coating inner surfaces.
Cannulae - assemblies used in endoscopic surgery, are selectively insulated and lubricated with Parylene.
Substrate Requirements
![]()
Devices to be Parylene coated are required only to have
reasonable vacuum tolerance. Articles that emit appreciable quantities of
volatile components under coating conditions (pressures of about 0.1 torr
at room temperature) will interfere with incoming monomer and with the
growth of the Parylene coating. Apart from the vacuum tolerance issue,
Parylene coatings grow on most substrates regardless composition. On soft
polymeric materials (e.g., butyls, neoprenes, silicones, etc.), a
significant amount of Parylene growth is needed before the Parylene
coating develops full properties. Over hard, inorganic surfaces such as
metals, glass, and ceramic, pretreatment of the surface may be needed to
obtain satisfactory adhesion of the Parylene coating.
The SCS Parylene Advantage
SCS Maintains FDA Device and Drug Master Files. Medical device manufacturers using SCS Parylene are able to reference Specialty Coating Systems’ FDA Drug and Device Master Files in their IDE, PMA or 510(k) sub-missions.
SCS offers Parylene C as a U.L. Recognized Component.
SCS offers USP Class VI Plastics Certification for Parylene N and C.
SCS presents tailored Parylene seminars on customer premises.
SCS operates multiple domestic and international coating centers, insure worldwide support and an ongoing knowledge base.
SCS has a full-time medical product manager with extensive medical device industry experience who can assist SCS medical customers with questions and procedures.
Copyright and Disclaimerc © Xuan Bao Hao Corp. 隱私保護及安全聲明 | 智慧財產權 請使用IE 4.0以上版本之瀏覽器